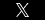The law treats children differently in many respects.
In criminal courts, for example, juvenile courts aim for rehabilitation rather than punishment.
In civil court, children are often granted exceptions in terms of their understanding of danger and liability. One example of this is seen in the doctrine of attractive nuisance. The principle holds it is the property owner’s responsibility to protect children from on-site hazards that may be present and which might be attractive to children and yet inherently dangerous. The theory holds children are naturally curious and not yet fully developed enough to recognize certain dangers and protect themselves in the same way we might expect adults to do.
 South Florida Injury Lawyers Blog
South Florida Injury Lawyers Blog